The
|
Input:
| Geometry requirements | A minimum of four points that nominally lie on a common radius |
| Specification Limits | Recommended |
| Description | Optional |
| Direction | Required |
Output:
•Pick the vector direction, normal to the circular surface.
•The points will be projected on a plane in the vector's direction.
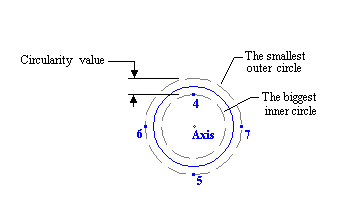
•The program will find the center of a circle based on the diameter of the smallest circle that contains all points.
•The program will calculate the diameter of the biggest inner circle, using the same center as determined by the smallest circle, that has all points outside of it.
•The circularity zone is the area between the two circles.
•The circularity value is the difference between outer circle radius and inner circle radius.
•This measure may produce incorrect Contributor Analysis or GeoFactor Equation-Based results, see Analysis Comparison & Assumptions.
Notes:For best results, users can apply |