The purpose of the
|
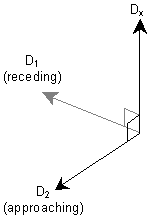
Dx = D1 X D2
D1 = first of two screen directions input from the dialog
D2 = second of two screen directions input from the dialog
Dx = calculated output vector associated to a set of points as their associated directions. Dx is perpendicular to D1, perpendicular to D2, and is pointed in the direction determined using the right-hand rule.
Objective
Compute the unitized vector cross-product of two unit screen directions
Apply the computed vector to a set of object point(s) as their associated vectors
Inputs
Object Point List:
A minimum of one object point. No maximum number of points.
O1 O2 O3 …On Set of Object point(s); any number equal or larger than 1.
Directions:
Two (2) screen directions defined from the dialog.
D1 D2 Set of screen vector direction(s).
Note: Requires a minimum of 1 ObjPt, and 2 Dir.
Assumptions
All directions are unit vectors.
Limitations
This routine outputs 0, 0, 0 for two input vectors that are parallel.
This routine outputs 0, 0, 0 for two input vectors that are opposing.
Test Cases
| A. | [1 0 0] X [0 1 0] |
Acceptance Criteria: Output should equal [0 0 1]
| B. | [skewed] X [another skewed] |
Acceptance Criteria: Output should equal [skewed & normal to both input vectors]
| C. | [skewed] X [parallel to first vector] |
Acceptance Criteria: Output should equal [0 0 0]
| D. | [skewed] X [opposed to first vector] |
Acceptance Criteria: Output should equal [0 0 0]