Truncation is used to eliminate the data outside a tolerance range. All 3DCS Tolerances and GD&T can have their range truncated.
This option can be applied knowing that the input shouldn't exceed the limits.
|
Related Topics:
|
Truncating Size Tolerances:
When applying truncation to a Size Tolerance, you are truncating the deviation of the hole/pin size, within its range or a desired range.
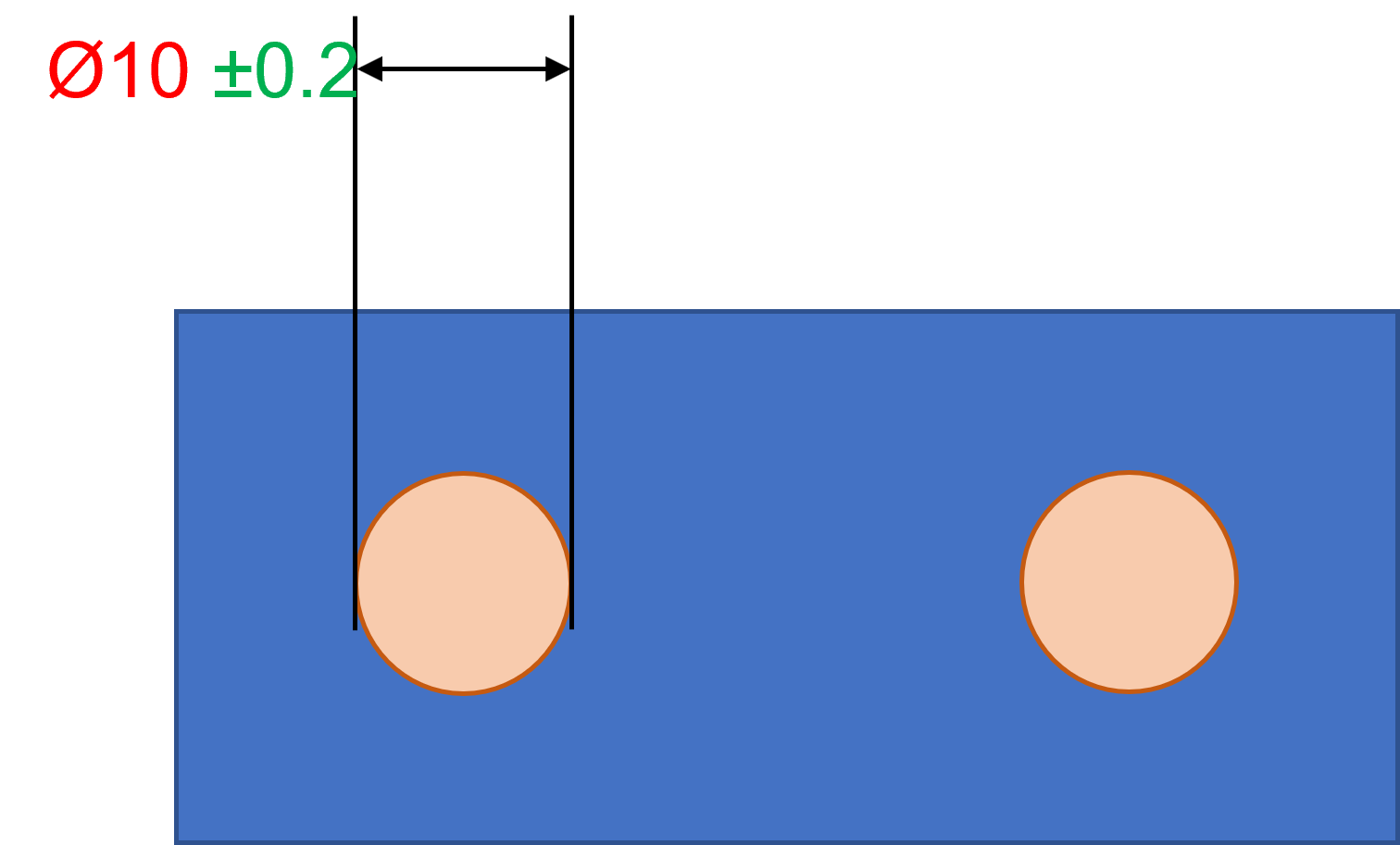
Fig. 1 Size
|
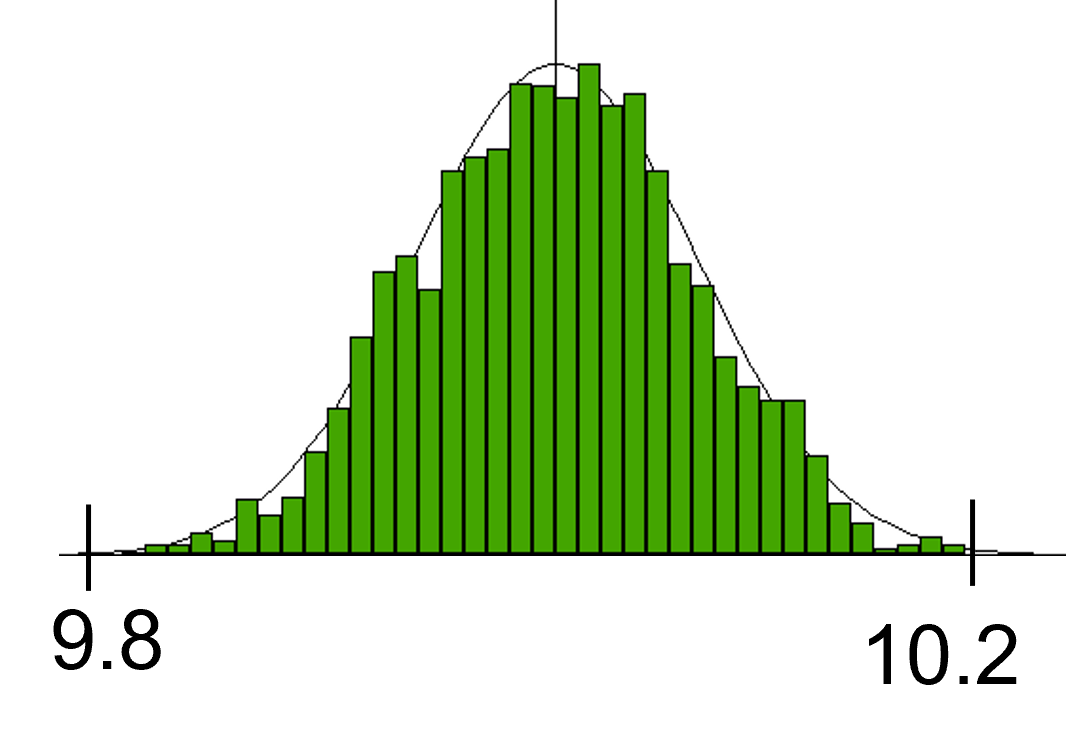
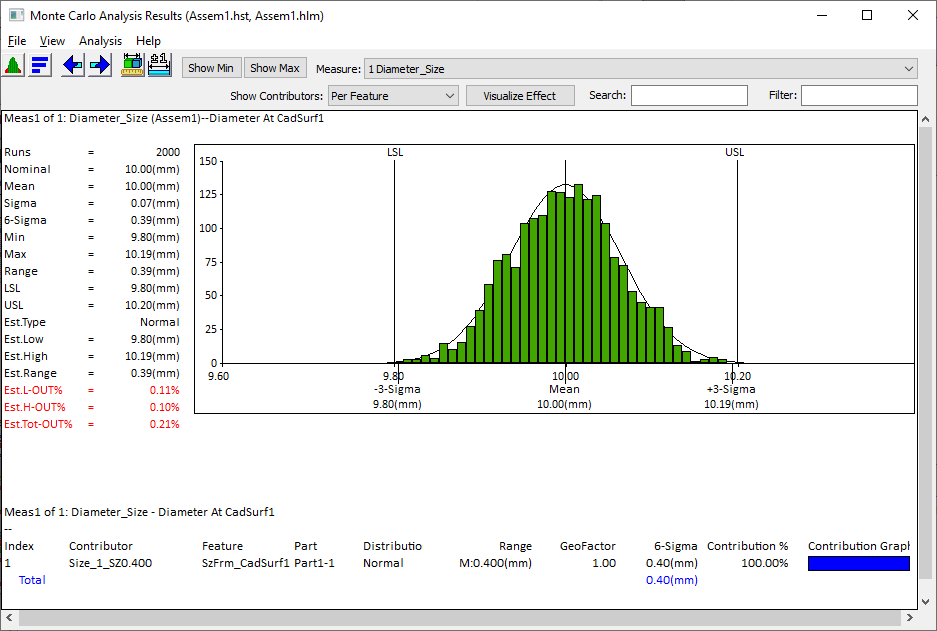
Fig.2 Size results |
In Fig.1, the Size of the hole is 10mm, with a tolerance of ±0.2. The Truncation should be active for the Max and Min Truncation fields, with +0.2 for the Max Truncation, and -0.2 for the Min Truncation. This would only show results within a range of ±0.2.
Users can confirm the results of a Truncated Tolerance by activating the Statistical output called Est.L-OUT%, Est.H-OUT%, and Est.TotOUT% in the Monte Carlo results window. Data should not exist from the Size Tolerance in the results.
Truncating a Geometrical Tolerance (Circular, Linear or GD&T)
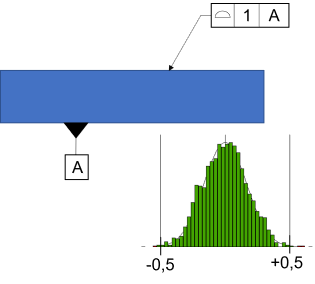
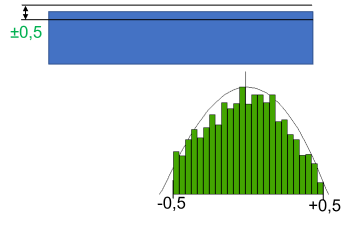
Truncating a Geometric Tolerance, like Profile or Position, could change the look of the Histogram and the Estimated Curve type. The Profile originally shown a curve type of Normal, but with the Truncation option active, the curve type changed to a Pearson I curve. This is due to the data being squished within the Truncation range, like in Fig.2.
In Fig.1 shows that statistical data can exist outside the limits.
Fig. 1 Profile
|
Fig.2 Profile results |