The See also: |
How to apply a GD&T Concentricity Measure
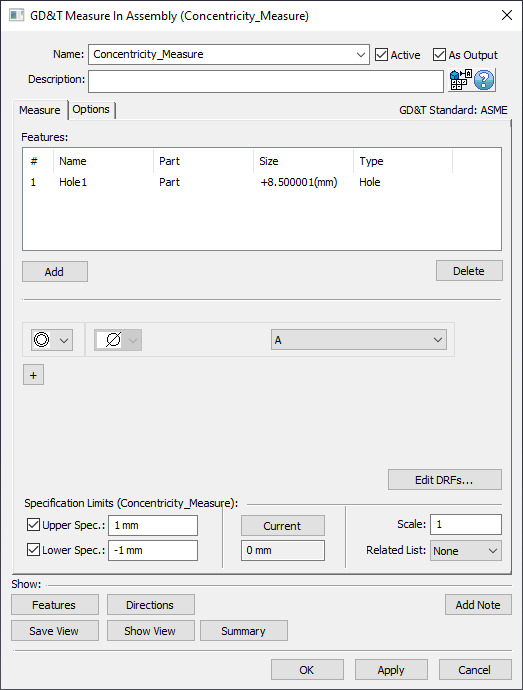
Procedure: 1.Create a new 2.Assign the new GD&T Measure a Name and Description (if desired). 3.Select [Add] and select any features from the graphics window or the Model Navigator that will be included in the Concentricity Measure. When finished select [OK][Close] in the Pick FeatureSelect dialog. 4.Select 5.Select the desired DRF from the DRF list. Note: if needed, define the DRF by selecting [Edit DRFs...]. Also Create Datums if needed. 6.Set the Upper Spec. Limit and Lower Spec. Limit to whatever values this measure is meant to check against (typically found on Assembly level drawing). Note: Can also turn off Upper Spec. Limit and Lower Spec. Limit if desired.
|
|---|
GD&T Concentricity Measure Analysis
Single Point Analysis: The
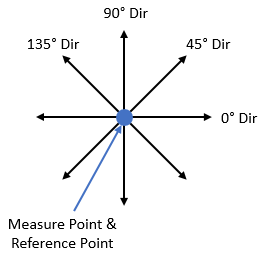
Above: At Nominal these are the measure directions 3DCS will use for the four Point Distance Measure that combine into the Concentricity Measure
Note: 3DCS does not display what these four directions of measure are for the
3DCS is not combining the four Point Distance Measures on a "per build" basis (like the Combination Measure does). Instead, 3DCS internally keeps these four measures and then only shows a single distribution at the end. The distribution shown is the one that returns the largest Recommended GD&T Value (see Recommended GD&T Value section for more details).
For an example case, we could have these four results:
In this case, the 90° direction has the largest Recommended GD&T Value so for the Note: Because 3DCS is only displaying Contributor Analysis results for one of the four directions, it is possible that there is a Contributor that is affecting the variation in one or more of the other three directions but is not displayed in the Contributor Analysis list for the measure because it is not adding variation to the measure direction that had the greatest Recommended GD&T Value.
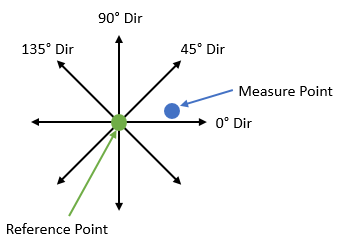
Multiple Point Analysis: When using multiple coaxial points in the Features list of the GD&T Measure dialog, the
For an example case, we could try adding two points to the Feature list and get these results:
The 45° direction of Point 2 has the largest Recommended GD&T Value and therefore it will be the output for this
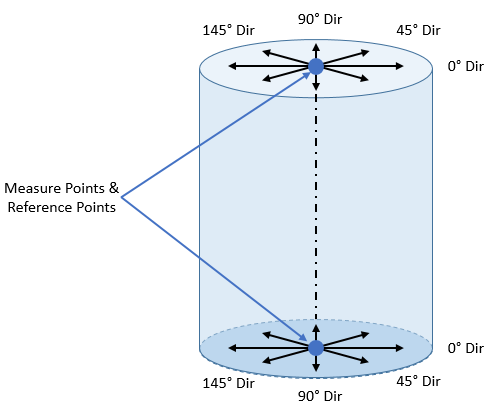
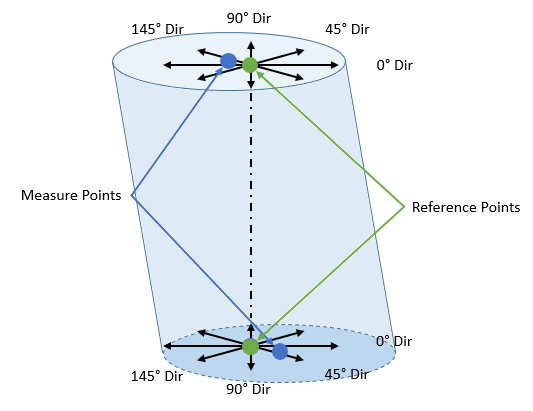
Single Axial Feature Analysis: An Axial Feature such as a pin or a hole can also be selected in the Features list of the GD&T Measure dialog. If a Feature has no Feature Points on the Center of the Feature, then the
Above: At Nominal these are the measure directions and points at the axis's ends that 3DCS will use for the Point Distance Measures that combine into the Concentricity Measure
For a single Feature without any Feature Points there will be eight total measures that the
For an example case, we could have these eight results:
The 0° direction of Axis End 1 has the largest Recommended GD&T Value and therefore it will be the output for this
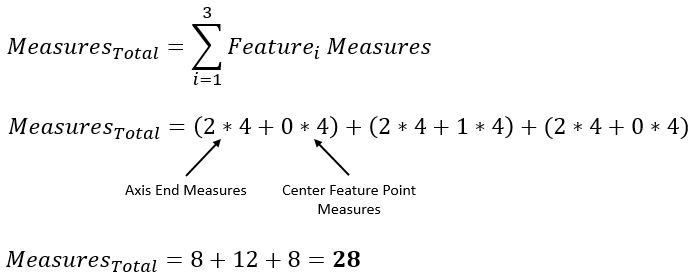
If the Axial Feature also contains Feature Point(s) on its axis, the
For an example case, we could have these twelve results:
The 135° direction of Axis End 1 has the largest Recommended GD&T Value and therefore it will be the output for this
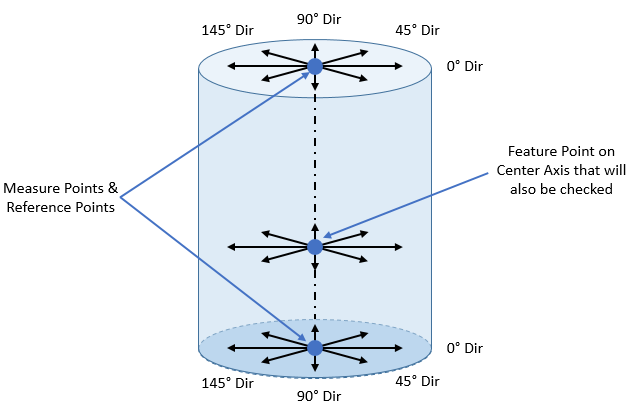
Multiple Coaxial Feature Analysis: Multiple Coaxial Features such as a pin or a hole can also be selected in the Features list of the GD&T Measure dialog. If a multiple Features are selected, then the
Example 1: 3 Features Feature1: 0 Center Feature Points Feature2: 1 Center Feature Point Feature3: 0 Center Feature Points
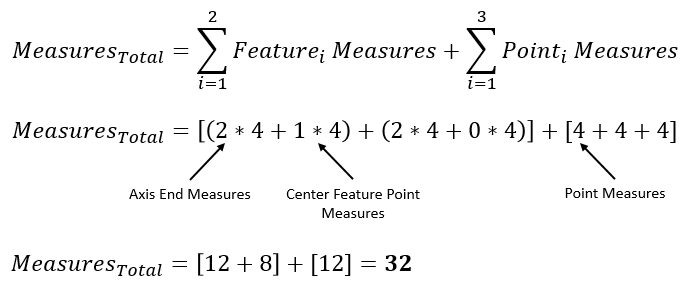
Example 2: 2 Features, 3 Points Feature1: 1 Center Feature Point Feature2: 0 Center Feature Points
For an example case, where we have two Features selected in the Features list and neither Feature has a Center Feature Point, we could have these sixteen results:
The 45° direction of Axis End 2 for Hole 1 has the largest Recommended GD&T Value and therefore it will be the output for this
|
|---|
Notes:•A requirement of using the |