With Feature Move using different types of features to locate parts, 3DCS validates the move by different set of Internal Cases.
|
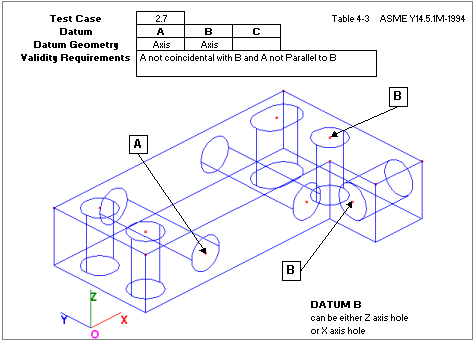
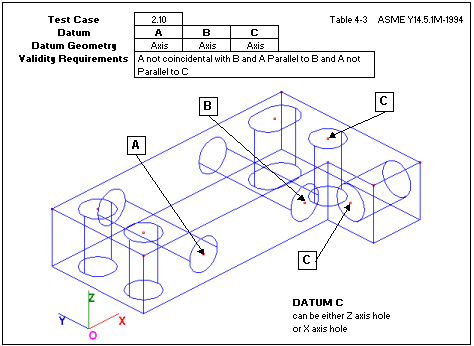
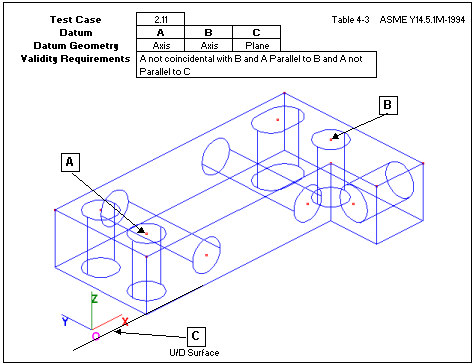
Uses two axes not coincidental or parallel.
|
|---|
|
|---|
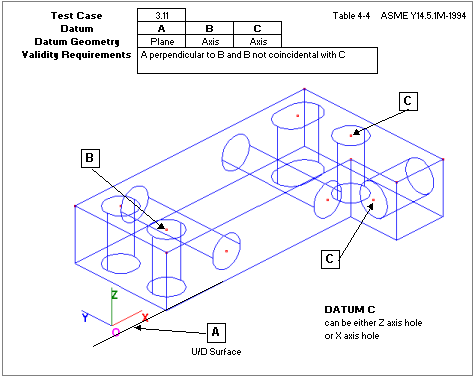
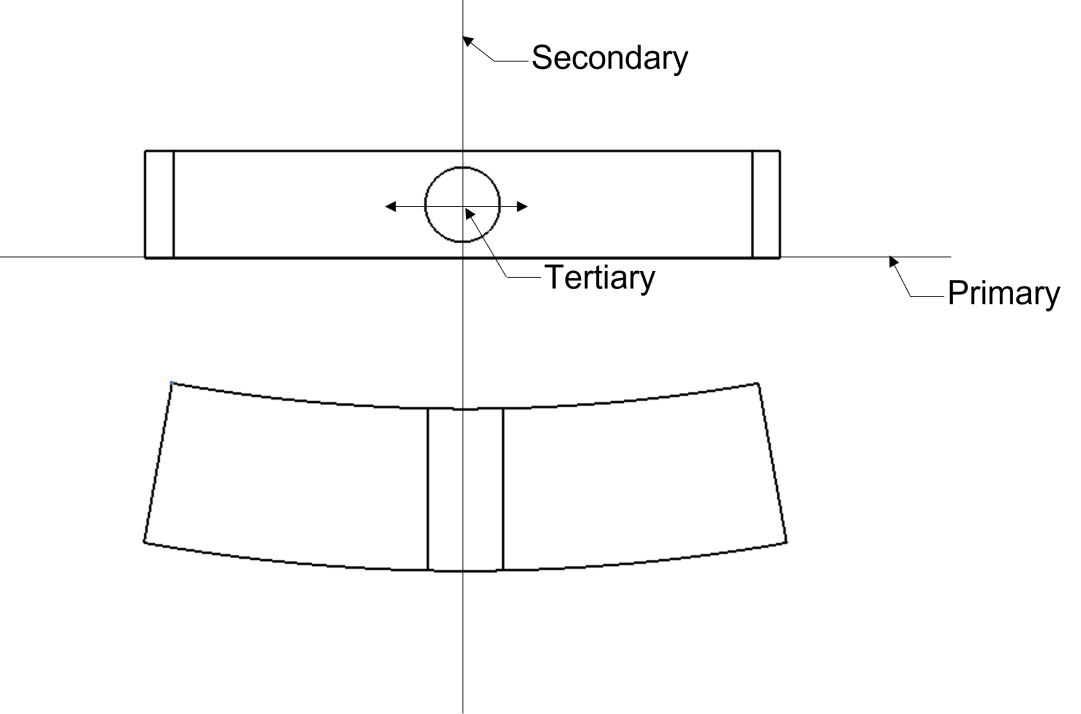
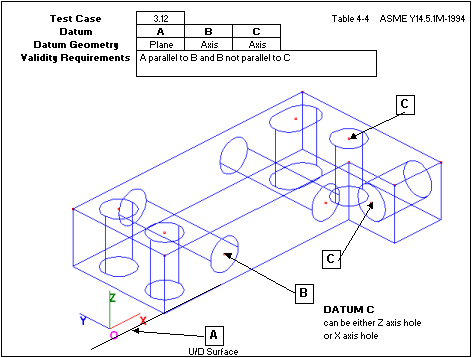
Case 3.11: Uses one plane and two axes, first axis perpendicular to the plane. The two axes are not coincidental.
Sub-case: Uses one plane and two axes:
|
|---|
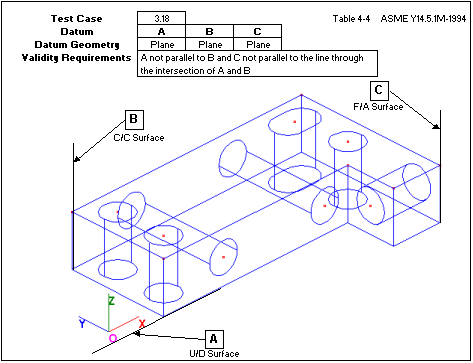
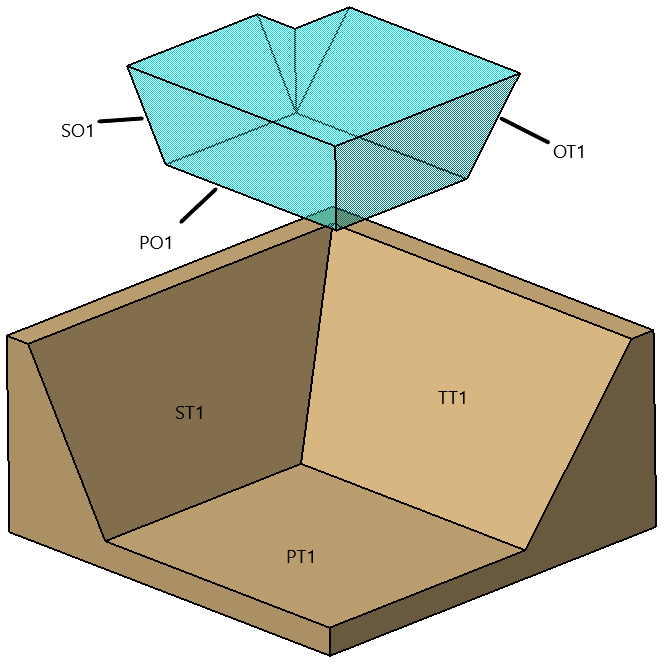
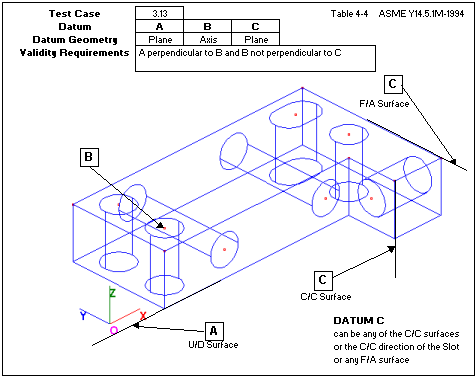
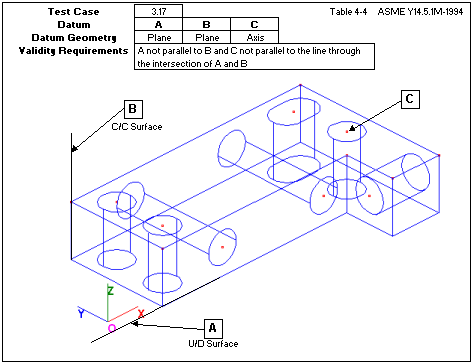
Uses three planes. The first two planes are not parallel to each other. The third plane is not parallel to the intersection line of the first two planes. (68479)
|
|---|
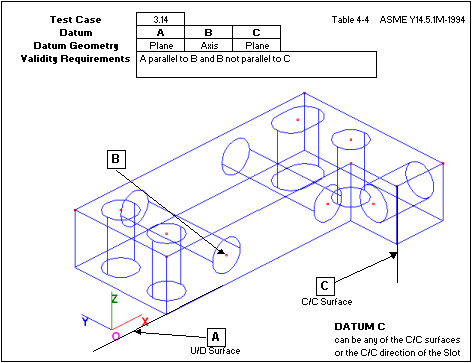
Uses one plane and two axes. CaseNum = 361 applies Nominal tilting for the Feature Move with (Pln1+Ax2+Ax3) DRF. (72581)
|
|---|
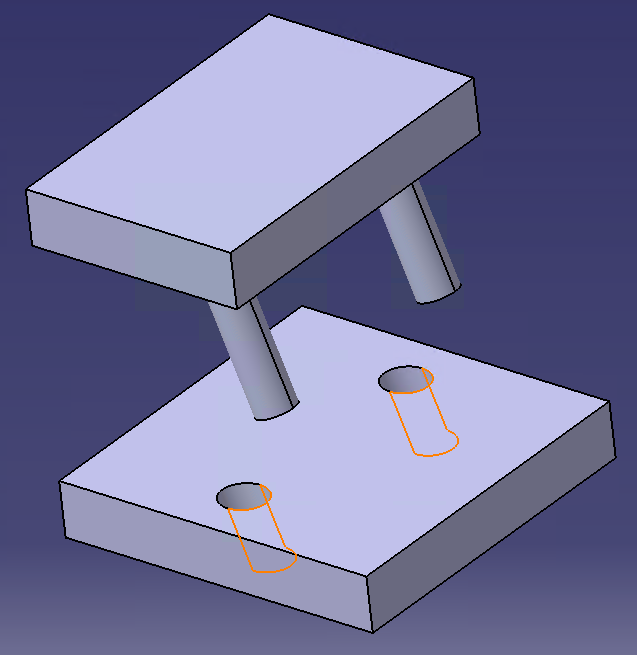
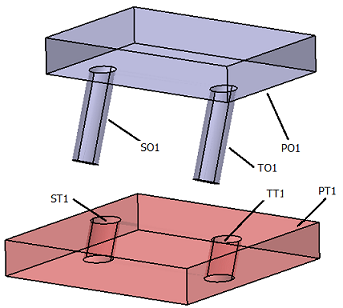
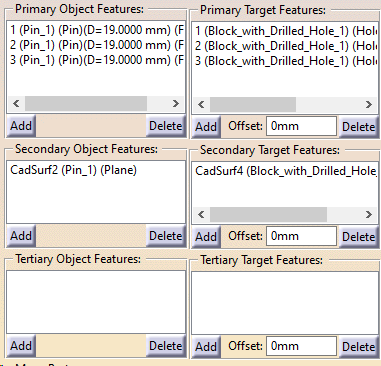
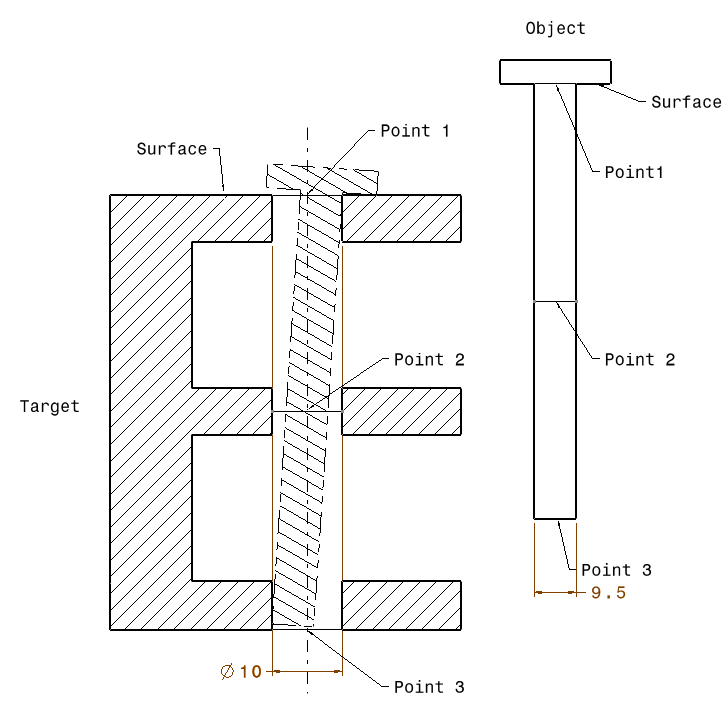
The effect of tilting the primary axis can be achieved with the Feature Move. (Ref. 65879). This case isn't typical but can be used to simulate a shaft going into a hole, and the shaft can tilt due to clearance and tolerances. Requirements •Primary Object and Target fields: o2 or more points along the axis; or use of Feature selected that represents Hole or a Pin Features. oPin example: Select the pin the same amount of times in the Primary field, with as many Target hole points. •Hole and Pin floats active in move.
|
|
|---|
1.) Uses two axes not coincidental or parallel.
2.) Uses three axes not coincidental, first two parallel with each other, but not parallel with the third axis.
3.) Uses two axes not coincidental, parallel with each other, and a plane for the tertiary control.
4.) Uses one axis, and a plane not parallel or perpendicular to the axis.
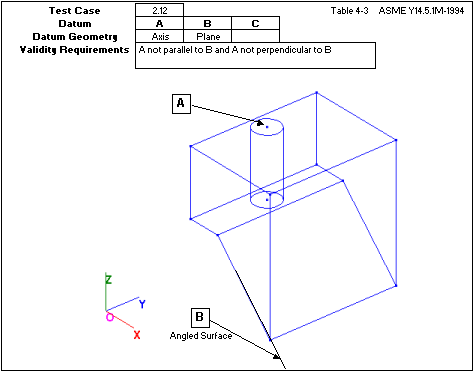
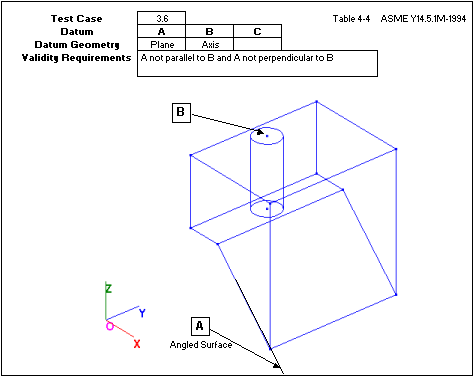
5.) Uses one plane and one axis not parallel or perpendicular to the plane.
6.) Uses one plane and two axes, first axis parallel to the plane. The two axes are not parallel.
7.) Uses one plane, one axis, and another plane for tertiary. First plane is perpendicular to the axis. The axis is not perpendicular to the tertiary plane.
8.) Uses one plane, one axis, and another plane for tertiary. First plane is parallel to the axis. The axis is not parallel to the tertiary plane.
9.) Uses two planes, and one axis. The two planes are not parallel to each other. The axis is not parallel to the intersection line of the two planes.
|
|---|
The Feature Move has three fields for users to select points or features. Here are the rules used to define how the Feature Move works, per Field: (ref: 65395, )
•Plane - Defined as LSQ Plane: if all selected features are defined as planar features (Non-features of size or Points with a Circle Size tolerance). (FM#1) •Plane - Defined as LSQ Plane: if all selected features are defined as planar features (Non-features of size, and coplanar.) (FM#3) oTreat as Axis-Plane if all features (2 or more) are Axis Type and not collinear. (FM#3-1) o LSQ Plane: if all selected features are defined as planar features (Non-features-of-size-edges, and the planar features are not co-linear.) (FM#3-2). •Axis - Defined as LSQ Axis: if all features are features of size, or edges, and all features are co-linear. (FM#2) •Average Method - Use the Average method with the feature type Plane or Axis from the first feature (Primary - First field). (FM#4)
|
|---|